Types Of Automation Used In Business Processes Today
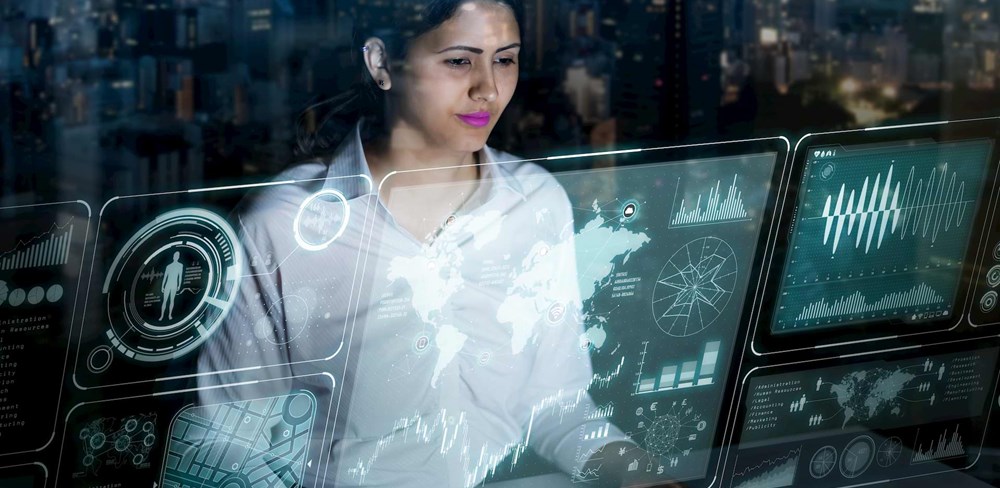
Process automation is evolving. Artificial intelligence isn't broadly practical yet, although automating complex work activities is possible and practical.
AI has shortcomings as a capable replacement for knowledge work, especially around knowledge representation, deduction, reasoning, problem solving, and learning. These are not sufficient for – or cannot be easily applied to – broad business uses, which shows the gap between AI hype and reality.
While waiting for AI, companies can use automated and machine analytic methods available to use today.
Partial Automation
Partial automation assists work actions performed by a person. Alerts, dashboards, and data entry automation (called robotic process automation or RPA) are examples of this. This kind of assistance facilitates but does not automate work, and its software development adds to IT complexity.
Machine and Deep Learning
Business has used statistical analytic methods for decades. Machine Learning automates them for work in real time while Deep Learning is an approach to successfully analyzing large, complex data sets like those used in image, audio, and video analysis. Both are essential for digital business.
Intelligent Process Automation
IPA is AI for now: IPA, while it may not automate highly complex process actions, automates less-complex yet significant units of work. Because business processes involve different organization units, IPA automates several related process actions and transforms the way work is structured.
Keys To Automating Business Process Actions
A process action is a unit of work that encompasses everything that can be done by one actor (a person or an automated process) in an uninterrupted period of time with resources at hand.
Process actions are the units of work in a business process, which means principles that guide work – like reviews, authorizations, and controls – need to be rethought so automated process actions include them.
Rethinking this work requires going deeper and clearly defining the necessary actions needed for an automated process to perform reviews, authorizations, and controls successfully.
Rules can be straightforward, ‘if-then’ constructs. Intelligent process actions require judgements that may use ‘if-then’ rules, but if that was all they did, automating them would be easy. Advanced rules employ machine learning and deep learning, otherwise they could not be automated. Rule management involves governing rule definition, deployment, and use.
Rules must be defined, managed, governed, and controlled so they can be universally available and applied consistently wherever and whenever they are used.
Here's more: How InfoNovus ensures consistent data and rules
Data is the fuel automation uses to function and it must be available in real time. As with rules, it is critical to manage, govern, and control data to be available wherever and whenever used. Typically, data in legacy applications and analytics require too much processing to standardize, integrate, aggregate, and prepare for use in automated process actions.
Data must be properly formatted and available in real time. Instant IT® applications produce data that is ready to use in automated process actions.
Here's more: How InfoNovus Instant IT keeps data ready-to-use
Analytics are the building blocks of automation. The challenge is to avoid making them difficult to identify, manage, and modify over time, like rules buried in code in a program. As with rules and data, analytics must be managed, governed, and controlled so they can be universally available and applied consistently in real time wherever they are used.
Analytics used for automation must be managed as a business asset and not as separate work products. They need to be elements of operating process designs.
Here's more: How InfoNovus operationalizes analytics
Algorithms have become synonymous with AI. Advanced algorithms like machine and deep learning analyze data, evaluate alternative options, and make decisions in real time. AI full-process automation is much more than that, and an algorithm is more than an analytic. While an automated algorithm, like an analytic, will be available and used in real time, it will be more complex and sophisticated in design.
Algorithms must be managed, governed, and controlled as business assets so they can be used consistently, correctly, responsibly, and effectively as elements of business designs.
Here's more: How InfoNovus applies automated analytics
Statistical, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, And Other Advanced Analytic Methods Are Used To Operationalize Process Automation
Process Automation uses many advanced, mathematical methods to automate work performed by process actions. Experience with developing, deploying, and managing advanced analytic methods and algorithms is necessary for digital business and establishes a foundation for using artificial intelligence, once it becomes practical, to automate complex processes.
Process Automation Improves Operational Productivity And Efficiency
While AI and advanced analytic technologies continue to develop, automation can provide a competitive edge and prepare companies for AI when it is ready. Companies can use technologies available today to automate business activities with process automation.

